This post was most recently updated on July 25th, 2023
Overview
Typhoid is an acute systemic infection characterized by continued fever. It is a serious communicable disease that can be transmitted from one person to another person through bacteria. It is also commonly known as enteric fever. The bacterium lives in the intestine of the human body and creates several intestinal disorders.
Occurrence
Typhoid is a mostly and widely spreadable disease that can be found throughout the whole place of the world. In the area like having a lack of sanitation and poor standards of drinking water, this is the common disease among the people.
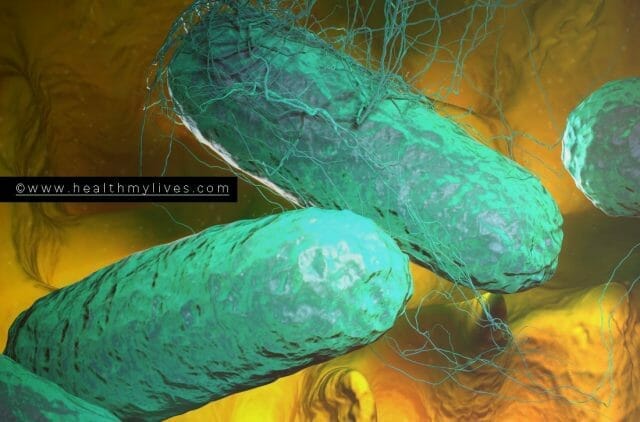
Causative Organism
The causative agent of typhoid is a bacterium, Salmonella Typhi. It is a rod-shaped, motile, gram-negative, bacillus bacterium measuring about 1.0 to 1.5µ in length.
What are the sources of infection of typhoid?
Salmonella typhi is restricted to the human body. Both the patients and carriers serve reservoir. The source of pollution is urine and faecal matter of tainted persons. The carrier state is most common among persons over forty years of age, especially females.
Incubation Period
The incubation period is variable, generally extending from one to three weeks. (It takes two weeks on average.)
What are the symptoms of Typhoid?
This is a severe disease, and it can affect different organs of the human body due to which symptoms may vary according to the situation of the patient. Some of the symptoms are given below:-
- The patient will have a constant fever lasting for one to three weeks.
- The fever may get worse when other organs or parts of the body like bone marrow, spleen or gall bladder are infected through the bloodstream.
- The spleen may have got enlarged and abdominal tenderness.
- The intestine will show lession, haemorrhage and ulceration. (Especially of Peyer’s patches.)
- Constipation may be more common than dehydration and diarrhoea.
- The appearance of rose spots may be seen on the trunk in some of the cases.
- As, we have already mentioned that, haemorrhages are also a symptom of this disease, the person may be caused to death by two to three per cent cases due to haemorrhages.
What are the possible preventions of typhoid?
The preventions of typhoid are as given below:-
- Disposal of sewage in a proper way.
- Maintain personnel cleanliness strongly.
- Public water supply needs to be protected, purified and chlorinated.
- Fly and insects need to be controlled by spraying some types of insecticides.
- Protecting food(such as a meal) and liquid(such as water and milk) from contamination is the mandatory step to prevent typhoid.
- You need to do proper treatment of raw fruits and vegetables before having them.
- Most of the people don’t have any idea about all the points mentioned above. So, we need to do a public awareness of people.
- Immunization with typhoid vaccine. (Tab: Typhyoil, Paratyphoid A, and Paratyphoid B) provides immunity for one to three years.
Treatments
Antibiotics like ampicillin and chloramphenicol are effective for the treatment of typhoid fever. We must continue treatment for several weeks to ensure the killing of bacteria. Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole and bumoxillin are excellent alternatives to ampicillin.