
The human body is intricate and complex, comprising various systems, organs, and tissues that work in tandem to keep us alive. Like every other body part, the genital region is no exception to undergoing changes and ailments over time, with lumps or bumps being a common concern many people encounter.
While some growths might be harmless and temporary, others may require medical attention.
In the journey to understanding the possible reasons for these changes, it’s essential to distinguish between the various causes. For instance, distinguishing between ppp vs genital warts is crucial, as each has a different origin and implications.
But before jumping to conclusions about any new growth or lump, it’s imperative to clearly understand the potential causes and when to seek professional help.
Read on to learn more.
The Causes Of Genital Lumps And Bumps
Before delving into the instances when you should see a doctor, it’s essential to learn some common causes of genital lumps and bumps. These include:
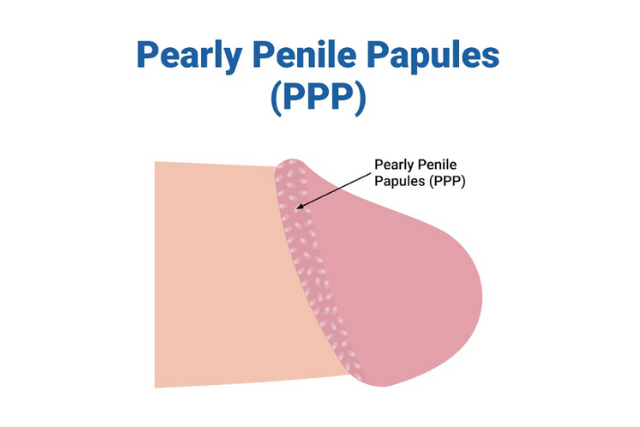
- Pearly Penile Papules (PPP): Also known as PPP, these are small, white, or flesh-colored bumps seen on the edge of the penis. They are benign and are not sexually transmitted. Importantly, they are not warts and are different from warts caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Genital Warts: These are flesh-colored or grayish growths that can appear on the genital area and are caused by certain strains of HPV. Unlike PPP, genital warts are contagious and one of the sexually transmitted diseases.
- Fordyce Spots: These are small, painless, yellow-white spots that can appear on the shaft of the penis or the labia. They’re merely enlarged sebaceous glands and are completely harmless.
- Bartholin’s Cysts: Found in women, these cysts develop when the Bartholin’s glands, located near the vaginal opening, get blocked. These cysts can sometimes be painful and might get infected.
- Molluscum Contagiosum: This is a viral skin infection that results in round, firm bumps. It’s mildly contagious and can be transmitted through direct skin contact, including sexual contact.
- Ingrown Hairs: After shaving or waxing, hair can sometimes grow back into the skin, leading to small, painful bumps.
Understanding these causes can guide you on when it might be time to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
When Should You Seek Medical Help?
Recognizing when a genital lump or bump warrants medical attention is essential for timely treatment and peace of mind. While some genital lumps or bumps may not be cause for concern, it’s essential to recognize when they might indicate something more serious. Consider seeking medical attention if you notice any of the following:
- Persistent Growth: Lumps or bumps may appear and disappear as part of natural body changes. However, if a bump remains for more than a few weeks or if you notice it increasing in size, it’s crucial to get it examined. Persistent growth could be a sign of an underlying condition that requires treatment.
- Pain Or Discomfort: While some growths are painless, any that cause significant pain, itching, burning, or discomfort should be a cause for concern. Pain or discomfort can be indicative of infections, inflammations, or other conditions that may require medical intervention.
- Unusual Appearance: Any bump that bleeds, has a rough or irregular texture, changes color, or appears ulcerated needs to be checked. These could be signs of more severe conditions, including certain types of cancer or precancerous lesions.
- Multiple Symptoms: If a lump or bump is accompanied by other symptoms, it’s a signal to see a medical professional. For instance, symptoms such as fever, genital discharge, swelling, redness, unexplained weight loss, or fatigue in conjunction with a lump could point to a more serious underlying condition.
- History Of Sexual Exposure: If there’s been recent sexual exposure, especially if unprotected or with a partner known to have a sexually transmitted infection, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. Some lumps, like genital warts, can be indicative of a sexually transmitted disease.
- Change Over Time: If a previously benign-looking lump starts to change – in color, size, texture, or any other aspect – it’s important to seek medical attention. This change could indicate a transformation from a benign condition to a malignant one.
- General Health Decline: If you notice a general decline in your health or well-being accompanied by the appearance of lumps, it’s advisable to see a doctor. Symptoms like fatigue, recurrent infections, or a decrease in overall vitality in conjunction with a genital bump could be a sign of systemic conditions.
- Recurrence After Treatment: If you’ve previously had a lump treated or removed and it reappears, it’s best to revisit your healthcare provider. A recurrence might indicate an incomplete treatment or a persistent underlying cause that needs further attention.
Recognizing these signs and responding proactively can ensure that any potential issues are addressed promptly. It’s always better to err on the side of caution, especially when it comes to your health.
Conclusion
While the presence of a lump or bump in the genital area can be alarming, it’s essential to remember that not all are harmful or indicative of a severe condition. By keeping the information mentioned above in mind and consulting a healthcare professional when in doubt, you can ensure you’re taking the best possible care of your genital health.


